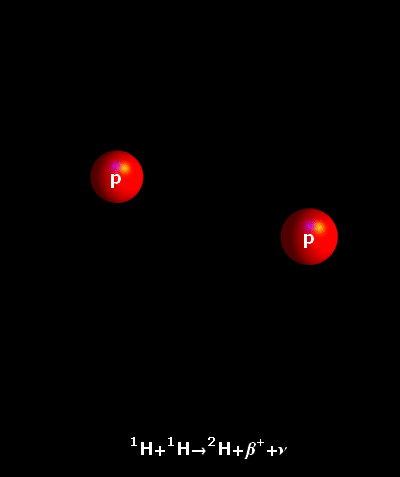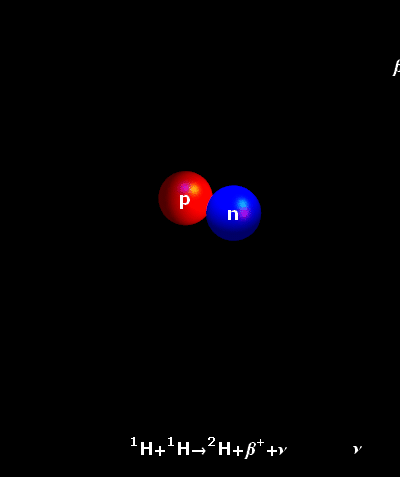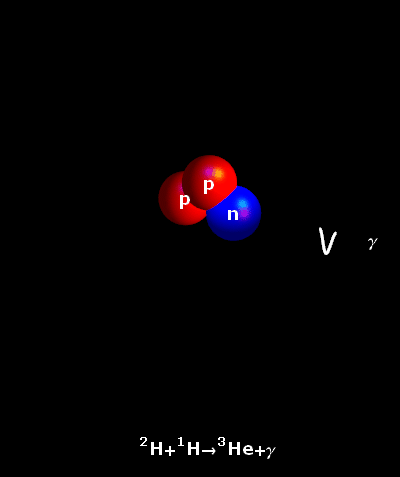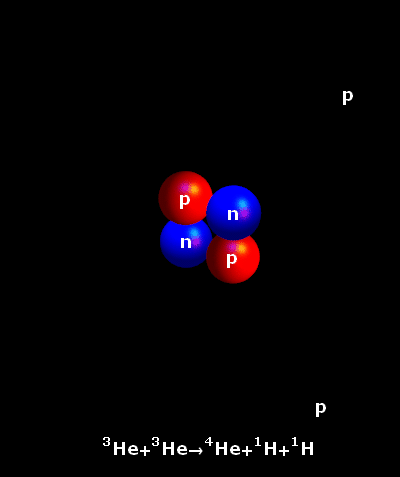
In the cores of stars like the Sun, energy is generated in a fusion
reaction called the proton-proton chain. In this process, two protons
come together so fast that they overcome their mutual electric repulsion
and fuse. Almost immediately, one of the protons turns into a neutron via
inverse beta decay, releasing a neutrino and a positron (antimatter
counterpart of an electon). The result is an isotope of hydrogen
called deuterium. From elsewhere, another proton flys in and fuses
giving off a gamma ray and forming an isotope of heliom called
helium-3. Another helium 3 from the environment flys in and fuses
to the other, forming a nucleus with 2 protons and 2 neutrons, and
giving off 2 protons to start the reaction again. The resulting
helium-4 is the byproduct of the reaction. Created by Jeff Bryant
(jeffb@wolfram.com)
|

